Introduction
Welcome to BuilderJS 6.0, the most powerful HTML web designer tool. BuilderJS is the easiest, quickest way to design elegant, mobile responsive HTML pages and emails for your business.
BuilderJS is built using pure JavaScript and HTML, making it easy to integrate with any web application, regardless of the server-side programming language (e.g., Java, .NET, PHP, Ruby on Rails, Python, etc.).
BuilderJS is fully customizable and designed for flexible integration scenarios. You can use it as a standalone application or embed it into your own web app, interacting with it through its simple and easy API. BuilderJS has been choosen by many popular frameworks as their HTML designer on the web UI.
Details of all available API methods are explained throughout this documentation.
System requirements
BuilderJS runs in a web browser and interacts with server-side scripts through standard AJAX requests and JavaScript methods that are supported by all modern browsers. That means BuilderJS can run on virtually any browser, including but not limited to:
- Google Chrome
- Mozilla Firefox
- Microsoft Edge
- Apple Safari
- Opera
BuilderJS may not be compatible with the legacy Internet Explorer: it might work, but functionality is not guaranteed. As a JavaScript-based application, BuilderJS is independent of both the operating system and the server-side scripting technology used.
Get quickly started
Sample virtual host configuration for Apache and Nginx to for the /var/www/demo document root
# Apache
<VirtualHost *:80>
DocumentRoot /var/www/demo
<Directory /var/www/demo>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
# Nginx
server {
listen 80;
root /var/www/demo;
index index.html index.php;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php8.4-fpm.sock; # Adjust version if needed
}
}
The installation process is explained in detail in the Installation section. However, if you'd like a quick preview of BuilderJS in action with its core features, simply follow this no-configuration installation guideline:
Step 1. Download the BuilderJS package you get from your purchase, it is a .zip file containing the core JavaScript files as well as a fully-working demo which helps you quickly get started.
Step 2. Extract the BuilderJS's .zip package and copy its
demofolder to your web server's document root, for example/var/www/demo. You can find in the right sample virtual host configuration for Apache and Nginx.Step 3. Make sure your Apache or Nginx web application server is running, then open the corresponding URL in your browser to launch the demo, for example:
http://localhost/demo/
That's it! You can now explore your own instance of BuilderJS hosted on your server like below:
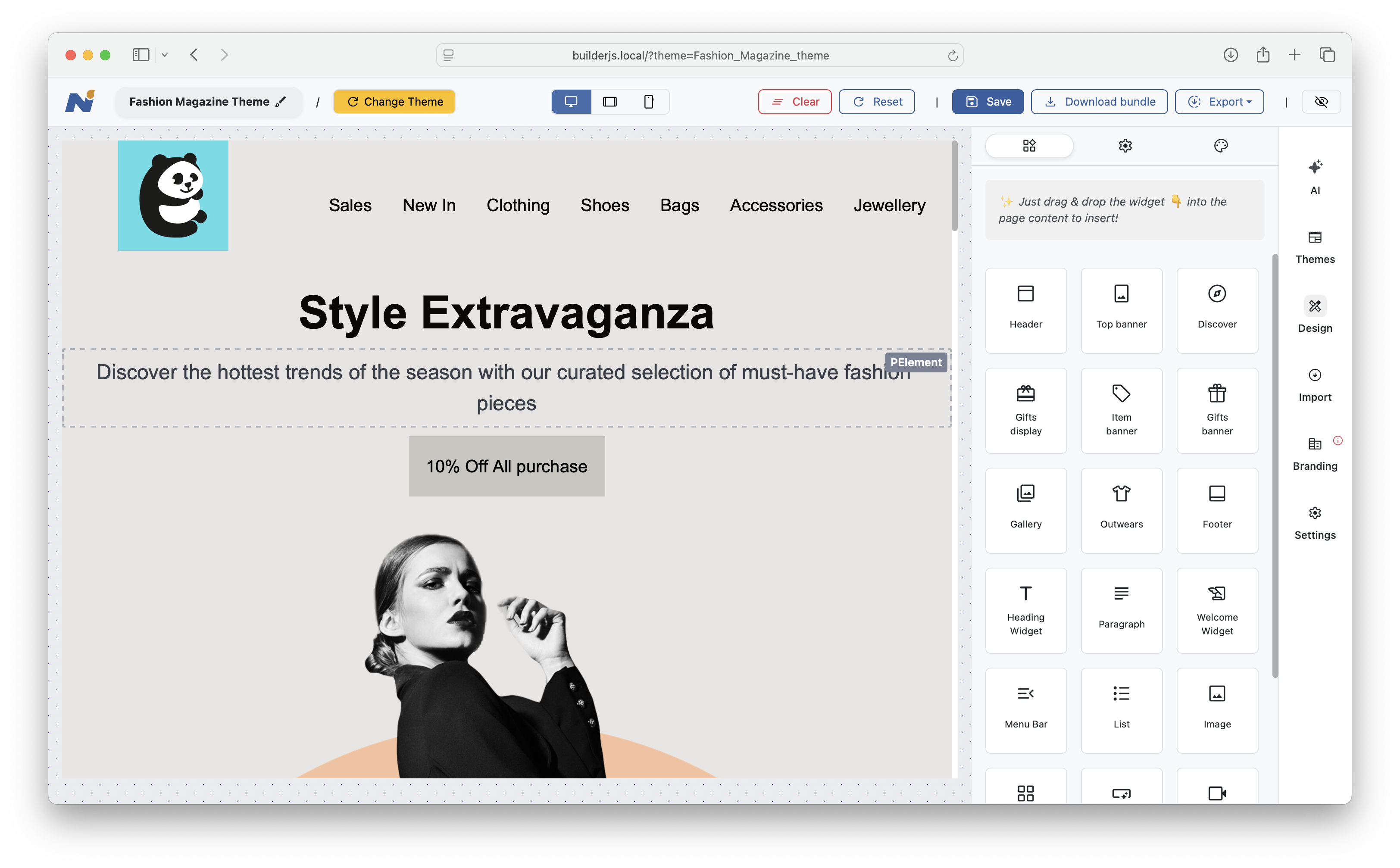
The demo includes a sample index.php file that loads the necessary BuilderJS resources. It also comes with with a default set of server-side scripts (written in PHP) to handle essential features such as Save and Export. You can use the provided PHP scripts as-is or implement similar functionality in any server-side language you're comfortable with, such as Ruby, Perl, .NET, Java, and more.
Installation
In the previous section, we provided a quick-start guide to help you run a demo installation of BuilderJS, allowing you to see how it works in your environment. In this section, we'll walk through a step-by-step guide to installing BuilderJS and configuring it to work with your server-side scripting.
There are two main parts to the installation:
The BuilderJS frontend (client side)
The server-side script
Explanation: BuilderJS runs entirely on the client side - in the user's browser - where it provides a visual interface for building beautiful HTML pages. However, when it comes to saving or publishing a user's design, you'll need to capture the output (the HTML content) and send it to a server-side script, which either saves the data or prepares it for download.
In the next section, we'll show you how to set up BuilderJS and include a demo illustrating how to capture its output and pass it to a server-side script for storage or export.
Include required files
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/builder/dist/builder.css"></link>
<script type='text/javascript' src="/builder/dist/builder.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script language="Javascript">
var builder = new Builder({
mainContainer: '#main',
settingContainer: '#idDiv3',
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
There are 2 files which are shipped with BuilderJS bundle
- builder.js - include all core functionality of BuilderJS
- style.css - the default styles for BuilderJS, used for its controls and dashboard.
Optionally, you can include Bootstrap CSS to improve userbility experience.
Once you have included BuilderJS .js file, the next step is to write JavaScript code to initalize the Builder. The example code on the right to see how to initalize a builder object with minimum configuration. After this step, you will have a builder object available for rendering in the next step.
Create a new page
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/builder/dist/builder.css"></link>
<script type='text/javascript' src="/builder/dist/builder.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script language="Javascript">
var builder = new Builder({
mainContainer: '#main',
settingContainer: '#idDiv3',
themeUrl: "/myAwesomeTheme/", // required by init() function
});
builder.init(theme = "/theme/abc");
</script>
</body>
</html>
Now it's time to load the builder in your browser.
If you want to start with a blank page for a new page design, execute the init() function. See the example code in the right panel.
Note the themeUrl parameter in the constructor method, this is required to initialize a new page. In BuilderJS, every page is created based on a theme, which consists of a set of related styles and page elements.
If everything is configured correctly, the builder interface will be rendered in your browser, and a sample page like the one below will be loaded:
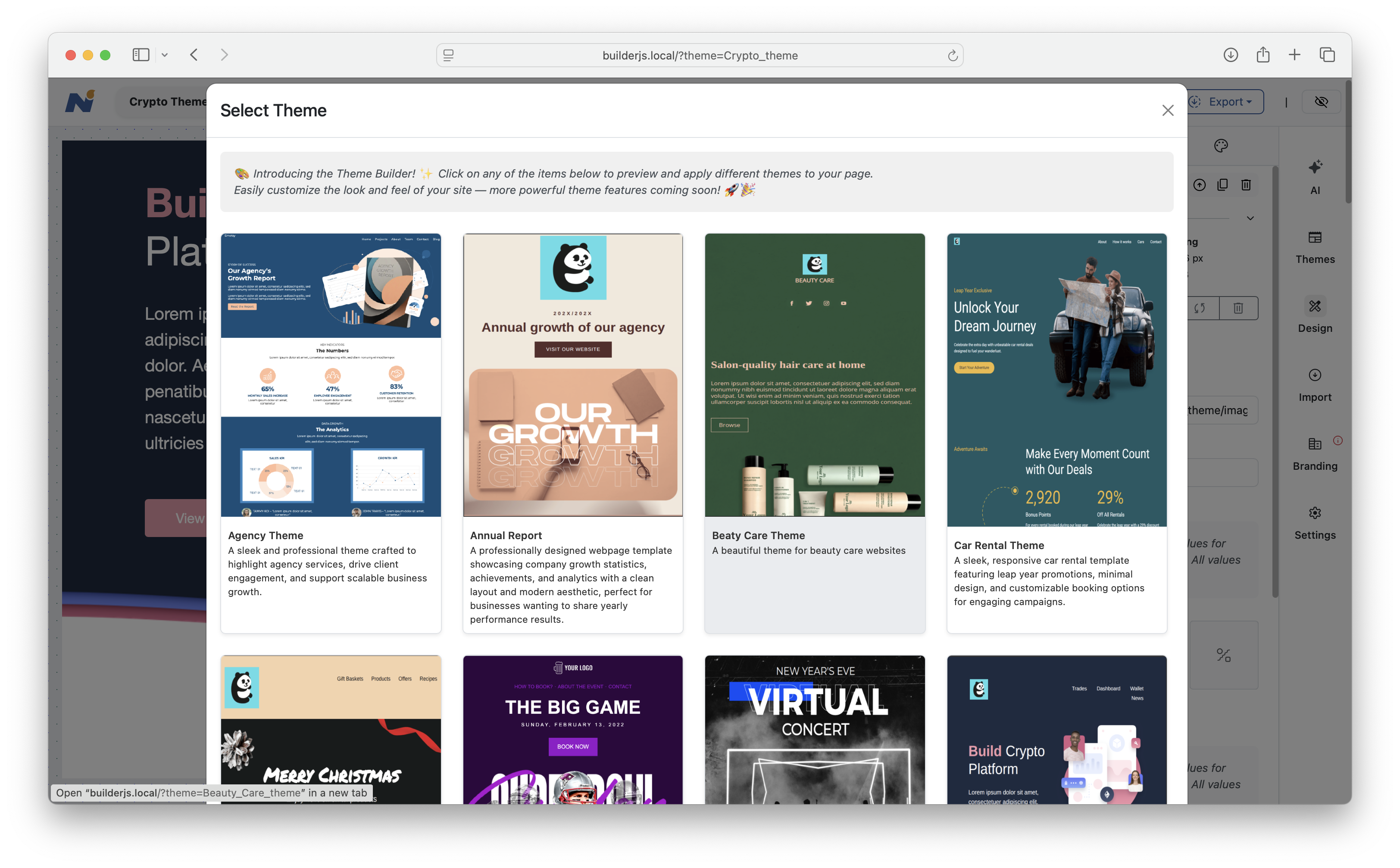
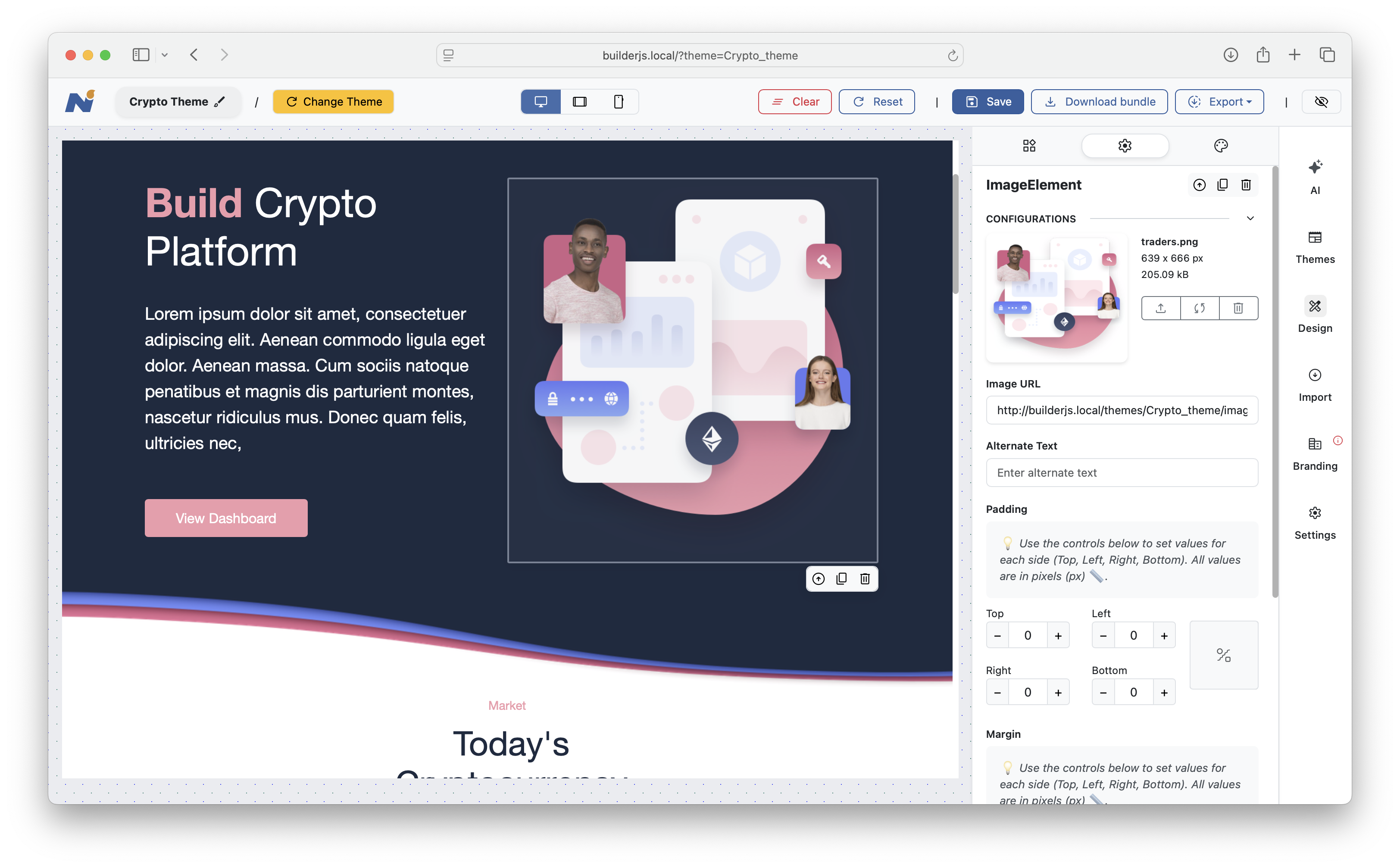
Another sample:
Open a page
Rather than starting from a blank page, you'll often want to load previously saved work to continue designing. BuilderJS supports multiple ways to load HTML content into the builder view.
From JSON string
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/builder/dist/builder.css"></link>
<script type='text/javascript' src="/builder/dist/builder.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script language="Javascript">
var builder = new Builder({
mainContainer: '#main',
settingContainer: '#idDiv3',
});
var data = "<?php echo file_get_contents('/data/Pages/MyPage.json'); ?>";
builder.load(data);
</script>
</body>
</html>
In this example, the data variable contains the entire JSON representation of an HTML page as a string. This string is then passed to the builder's load function to display the content in the browser.
BuilderJS pages are stored in JSON format, which can be saved in any type of storage - such as the file system, a relational database (RDBMS), and more. Later, the stored JSON can be loaded back into the design view.
Don't worry about the JSON format or how to generate it - this will be explained in the Storage section below.
From URL
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/builder/dist/builder.css"></link>
<script type='text/javascript' src="/builder/dist/builder.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<script language="Javascript">
var builder = new Builder({
mainContainer: '#main',
settingContainer: '#idDiv3',
});
var url = "http://example.com/pages/MyPage.json";
builder.loadFromUrl(url);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Instead of loading the entire JSON data into a JavaScript variable as shown earlier, a more convenient approach is to use the loadFromUrl() method to fetch JSON content from a remote URL.
For example, if your page's JSON data is stored on a server and accessible at http://example.com/pages/MyPage.json, you can load it using this method as shown in the example.
Don't worry about the JSON format or how to generate it - this will be covered in the Storage section below.
Below is a summary of the constructor parameters for BuilderJS:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| mainContainer | The ID of the HTML element into which the builder design will be rendered |
| settingContainer | The ID of the HTML element into which the builder settings will be rendered |
| themeUrl | URL of the theme folder. BuilderJS comes with many themes and even more themes are coming. |
| assetUploadHandler | URL of the server-side script which handles assets uploading |
| aiHandler | URL of the server-side script which handles AI features. See our example writen in PHP for reference. |
Configure server script
Setting up BuilderJS involves certain steps, especially when configuring the page that wraps around it and interacts with it. However, this is intended by design: BuilderJS is built to be fully customizable.
For example, BuilderJS does not include any default SAVE or EXPORT buttons. You will need to add these buttons yourself and handle their click events. When the user clicks a Save button, it should call the builder's getJson() API method to retrieve the current design. From there, it's up to you to handle the result-for instance, by sending it via an AJAX request to a server-side script that saves it to local storage, a database management system (DBMS), or remote storage such as AWS S3.
By creating the buttons yourself, you're not limited to BuilderJS's default style-you're free to place them anywhere on your page and style them however you like.
Save
Click on PHP, Ruby or Python tab to see how to implement SAVE operation with a server-side script
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<body>
<button id="btnSave">Save</button>
<script>
// Function that handles saving
function save() {
var data = builder.getJson();
$.ajax({
url: 'save.php', // Your server-side script
data: {
page_id: 'Page #ID',
data: builder.getJson(),
}
success: function (response) {
console.log("Save successful:", response);
},
});
}
// Assign click event
document.getElementById("btnSave").addEventListener("click", save);
</script>
</body>
</html>
import mysql.connector
from flask import Flask, request
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/update', methods=['POST'])
def update_page():
page_id = request.form['page_id']
data = request.form['data']
conn = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="user",
password="password",
database="myDB"
)
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = "UPDATE pages SET data = %s WHERE id = %s"
cursor.execute(sql, (data, page_id))
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
return "Saved successfully"
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
# Sample controller code for handling the save request
# sent from BuilderJS
require 'activerecord'
require 'mysql'
# Set up MySQL connection
ActiveRecord::Base.establish_connection(
adapter: 'mysql2',
database: 'myDB',
username: 'user',
password: 'password'
)
# Associate Template class with the `templates` data table
class Template < ActiveRecord::Base
# associated with `templates` table
end
# Retrieve parameters passed to the server script
content = params[:content]
template_id = params[:id]
# Actually update the MySQL database
template = Template::find(template_id)
template.content = content
template.save
<?php
// Sample controller code for handling the save request
// sent from BuilderJS
// MySQL credentials
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "user";
$password = "password";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Retrieve parameters passed to the server script
$pageId = $_POST['page_id'];
$data = $_POST['data'];
// Actually update the MySQL database
$sql = "UPDATE pages SET data = '{$data}'
WHERE id = '{$pageId}'";
if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) {
echo "Saved successfully";
}
$conn->close();
Once you have initialized the builder and either loaded a template or started a new page, you can begin designing your pages. To save your current work for future editing, you need to capture the current data from BuilderJS and store it in a system such as a filesystem or MySQL database.
Since BuilderJS is a pure JavaScript application running in the browser, it does not store any data by itself - this is where a server-side script becomes necessary. The most common approach is to use BuilderJS's getJson() API method to capture the current state, then send the resulting data to a server script via Ajax for storage. In this example, we provide backend handlers implemented in PHP and Ruby, though you can use any programming language you prefer. The key point is capturing and handling the input.
Click the php or ruby tabs in the code sample panel to see the details. Refer to the example on the right to understand how this works in practice.
Summary of steps:
- Load BuilderJS
- Create a new page to design
- Add a "Save" button that, when clicked, retrieves the builder data and sends it to the server's save.php script, which stores the HTML content in a MySQL database.
Instead of storing builder data to MySQL, you are free to handle it any way you want in your server-side script.
Export and download
<script>
function export() {
$.ajax({
url: 'export.php',
data: {
html: builder.getHtml(),
},
success: function (response) {
console.log("OK");
}
});
}
</script>
<?php
$html = $_POST['html'];
$filename = "My-Awesome-Design-" . date("Ymd_His") . ".html";
// Set headers to force download
header('Content-Type: text/html');
header('Content-Disposition: attachment; filename="' . $filename . '"');
header('Content-Length: ' . strlen($html));
echo $html;
require 'sinatra'
require 'time'
post '/download' do
html = params[:html]
timestamp = Time.now.strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
filename = "My-Awesome-Design-#{timestamp}.html"
content_type 'text/html'
headers 'Content-Disposition' => "attachment; filename=\"#{filename}\""
body html
end
from flask import Flask, request, Response
import datetime
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/download', methods=['POST'])
def download():
html = request.form.get('html', '')
timestamp = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
filename = f"My-Awesome-Design-{timestamp}.html"
response = Response(html)
response.headers['Content-Type'] = 'text/html'
response.headers['Content-Disposition'] = f'attachment; filename="{filename}"'
response.headers['Content-Length'] = str(len(html.encode('utf-8')))
return response
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
The next common task is exporting the page for real-world use. Once users finish their design and click the Export button, the final HTML content is sent to a server-side script that handles the export process-typically via an AJAX request. See the example on the right.
BuilderJS provides a getHtml() method that captures the final HTML of the designed page.
After receiving the HTML content, the server script can save it to a file and make it available for download. The exported HTML file can then be uploaded to a hosting environment as a normal HTML page.
Make inline CSS
<?php
require 'vendor/autoload.php';
use TijsVerkoyen\CssToInlineStyles\CssToInlineStyles;
$html = $_POST['html'];
// DOM parse to extract and load external CSS files
libxml_use_internal_errors(true);
$dom = new DOMDocument();
$dom->loadHTML($html, LIBXML_HTML_NOIMPLIED | LIBXML_HTML_NODEFDTD);
libxml_clear_errors();
$xpath = new DOMXPath($dom);
$cssCombined = "";
// Extract and load all <link rel="stylesheet"> CSS files
foreach ($xpath->query('//link[@rel="stylesheet"]') as $link) {
$href = $link->getAttribute('href');
$css = @file_get_contents($href);
if ($css !== false) {
$cssCombined .= "\n" . $css;
}
$link->parentNode->removeChild($link); // Remove link tag
}
$html = $dom->saveHTML();
// Minify CSS (basic)
$cssCombined = preg_replace('/\s+/', ' ', $cssCombined);
$cssCombined = preg_replace('/\/\*.*?\*\//s', '', $cssCombined);
$cssCombined = preg_replace('/\s*([{};:>,])\s*/', '$1', $cssCombined);
$cssCombined = str_replace(';}', '}', $cssCombined);
// Inline CSS into HTML
$inliner = new CssToInlineStyles();
$inliner->setHTML($html);
$inliner->setCSS($cssCombined);
$inlinedHtml = $inliner->convert();
// Send as downloadable file
$filename = "My-Inlined-Design-" . date("Ymd_His") . ".html";
header('Content-Type: text/html');
header('Content-Disposition: attachment; filename="' . $filename . '"');
header('Content-Length: ' . strlen($inlinedHtml));
echo $inlinedHtml;
If the HTML design contains references to external CSS files, it is considered best practice to fetch those styles and apply them directly to the HTML content using inline CSS. This makes the HTML self-contained and more compatible with various browsers and email clients that may not support external CSS references. The inlining process can be handled by a server-side script and performed just before the HTML is downloaded. See the example on the right, which also includes CSS minification.
Features overview
Visual drag & drop designer
Build your perfect page with ease — simply drag and drop elements exactly where you want them. No need to write a single line of HTML code. Whether you're a designer, marketer, or just getting started, BuilderJS makes page creation fast, intuitive, and enjoyable. Focus entirely on your creative vision while the builder handles the underlying code, structure, and responsiveness — giving you beautiful results without the technical hassle.
Visual styling sade easy
Style your HTML page effortlessly with BuilderJS's intuitive visual controls. There's no need to learn or even glance at CSS code—just point, click, and adjust. Modify colors, fonts, spacing, borders, shadows, hover effects, and more with smart UI panels that respond in real time. Whether you're refining typography or creating subtle animations, our interface empowers you to bring your design ideas to life with pixel-level precision—all while maintaining clean, valid code behind the scenes.
Rich library of composite elements
Build faster with a rich collection of pre-designed, fully customizable composite elements. Choose from navigation menus, hero sections, pricing tables, testimonials, feature blocks, social icon sets, sliders, and banners—each thoughtfully designed and ready to use. Simply drag and drop components into your layout, then fine-tune them to match your brand or project requirements. These ready-made blocks help you create modern, professional layouts without reinventing the wheel, saving you hours of manual work.
Seamless Device Preview
Ensure your page looks stunning on every screen size with BuilderJS's responsive preview modes. Instantly switch between mobile, tablet, and desktop views to see exactly how your content adapts across devices. No guesswork, no resizing your browser—just real-time previews that reflect modern responsiveness standards. Fine-tune layouts and element spacing per device to achieve perfect results, whether you're designing a landing page, email, or a responsive website.
AI-Powered Content Assistance
Let AI accelerate your creative process like never before. BuilderJS's built-in AI assistant can automatically generate meaningful headlines, filler text, calls to action, and even full sections of your page content—all based on your instructions or theme. It can fix grammar, rewrite text, suggest better phrasing, and ensure a consistent tone across your design. Whether you're stuck on copy or in a rush, AI helps you move forward with quality content in seconds.
Universal Template Format
BuilderJS is powered by a flexible, human-readable markup language designed for real-world design and development workflows. Whether you're a designer looking to make your template editable or a developer integrating dynamic content, BuilderJS's format makes it easy. Convert your static HTML designs into reusable themes that work seamlessly inside the builder—complete with editable zones, smart components, and modular layouts. This universal format bridges the gap between creativity and productivity.
Clean & Semantic HTML Output
Every page you build with BuilderJS is backed by professionally structured, semantic HTML code—optimized for real-world use. Whether you're deploying to production, integrating with a CMS, or sending as part of an email campaign, you can trust the code is lightweight, accessible, and compliant with best practices. SEO experts, accessibility auditors, and developers alike will appreciate the minimalistic yet meaningful output, making integration and maintenance a breeze.
Revision History
Never worry about making a mistake again. BuilderJS includes powerful version history tracking, so you can experiment freely and revert back to any previous version of your design with a single click. Automatic saving ensures your work is protected in real time, and manual checkpoints let you capture key design milestones. Whether you're A/B testing layouts or fixing an accidental change, revision history gives you peace of mind and total creative freedom.
Theme & template
A theme consists of sample element templates that share a unified style. Every website or page in BuilderJS is based on a theme. In BuilderJS, a theme is actually a set of many HTML element templates that users can quickly drag and drop them into the page designer. Each theme comes with its own unique styles and a predefined set of HTML elements for users to choose from.
Some examples of HTML elements in a theme include:
- Menu bar
- Main banner
- Carousel banner
- About us block
- New features block
- Footer area
- Testinomial area
Users can simply choose an element, drag and drop it into the designer view, and modify the element's content to make up their own page.
In addition to the available templates in BuilderJS, you can also create custom themes to enhance your users' experience. To create a theme for BuilderJS, you'll need to understand its theme markup language and conventions. Generally, the process of creating an BuilderJS theme involves the following steps:
- Step 1: Design a visually appealing HTML template that includes all possible elements.
- Step 2: Break the template into smaller HTML components, each wrapped with BuilderJS's custom markup.
- Step 3: Publish your theme (the individual HTML components).
Detailed specifications and guidelines for working with themes are still in development. The BuilderJS team is actively working to release more themes for users every day. A comprehensive guide will be available soon to help development teams create their own themes with ease.
Common issues
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Page blank | When loading our pre-built demo folder, if you see that the page is just blank without any content, then it is very likely that the core files builder.js is not referenced correctly. Make sure you use the correct absolute or relative path to the file. |
| Element not found error | Sometimes, you might get a blank page with such message. Check the mainContainer parameter you pass to the builder and ensure it matches the valid ID of an HTML element that serves as the container for BuilderJS’s rendering. Notice that it should be an ID string which is compatible with CSS selector. |
| Page frozen | In certain cases, the browser may become frozen and unresponsive after a while. This is very likely caused by a JavaScript function running in an infinite loop. Often, the issue stems from event handler code, particularly the changed event. Make sure you do not execute long-running functions in your changed event handler, as this event is triggered very frequently during user interactions. |
| Styles broken | If the page loads but appears without proper styles, it’s very likely that the builder.css file is not correctly referenced. Verify that you’re using the correct path to the CSS file. |
| Error saving or exporting | Save and export operations are handled by server-side scripts. To debug issues, check your server’s log files for details. Alternatively, you can wrap your server script in a try/catch block to return readable exception messages to the browser. See the Error codes table below for a list of supported HTTP status codes. |
Customization
<script>
class MySampleWidget extends Widget {
// get HTML to insert into content
init() {
super.init();
}
title() {
return 'My Sample Widget';
}
renderHtml() {
return '<div> A Simple Widget with 1 line of text </div>';
}
// custom behavior goes here...
</script>
BuilderJS is written with a well-designed structure that allows for easy and straightforward customization. For example, you can add your own custom widget to the library alongside the default ones such as Text, Image, Video, Social Network Icons, and more. Check the right panel's JavaScript tab to learn how to create a custom widget.
By extending the Widget base class, your MySampleWidget will automatically inherit all the common widget behaviors like drag-and-drop functionality, and support for moving, duplicating, and deleting. You can also define its own characteristics, such as title and thumbnail, by overriding the corresponding methods.
Documentation is currently being updated. In the meantime, please contact us for more details on this topic.
API reference
API methods
Since BuilderJS is a pure JavaScript library that accepts parameters during initialization, it can be integrated with any programming language or database system.
Its main function is to load an HTML template, allow users to make changes via visual drag-and-drop or source editing, and then submit those changes to the server for further handling, communication is made by Ajax. You can use PHP, Ruby, Python, Java, .NET, or any other server-side scripting language to handle BuilderJS requests. The distributable package also includes sample PHP scripts for saving, exporting, and more. exporting, and more.
In the browser, you can interact with BuilderJS through its public methods
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
getJson() |
Retrieve the JSON content of the current page. Use this method to save your current work. i.e. pass to a server script for storing. This JSON data can be loaded into the builder later when a user opens an existing project. |
getHtml() |
Retrieve the HTML content of the current page. Use this method to capture the final HTML output of the builder to publish or export. |
select(id) |
Selects an element on the current page, specified by its unique id. This method is useful when you want to interact with a specific element in the current page. |
unselect() |
Deselects any currently selected element on the page. Notice that any unsaved change made to a selected element shall be discarded. |
getSelectedElement() |
Returns the currently selected element on the page. |
insertElements(list) |
Inserts a list of elements into the current page. This method is useful when you want to programmatically interact with the builder. |
addWidgets(item) |
Adds a new widget to the widget panel. This method is useful when you want to define your own custom widgets. |
load(json) |
Loads a custom page defined by the provided JSON structure. The JSON must comply with BuilderJS’s specifications and conventions. |
Events
<script>
// Sample event handling code that
// listens for an event and executes custom code when triggered
builder.addEventListener('loaded', function (event) {
console.log('The page has been loaded into BuilderJS!');
});
</script>
The following are BuilderJS’s events that you can watch for to detect changes and interactions within the editor:
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
initialized |
The builder has completed its initialization process and is fully ready for use. At this stage, all resources, configurations, and UI components have been loaded, allowing users or scripts to safely interact with the builder and start creating or loading pages. |
loaded |
A page has been successfully loaded into the builder. This event indicates that the builder has parsed the page content and rendered it visually in the workspace, making it ready for editing or further manipulation. |
modified |
An existing element within the page has been modified. This includes changes to attributes, styles, text content, or any other editable properties. This event is triggered whenever a user updates an element’s properties or appearance. |
inserted |
A new element has been added to the page. This occurs when a user drags and drops a new component into the layout or when an element is programmatically inserted via an API. The event signals that the page structure has expanded. |
deleted |
An element has been removed from the page. This event fires when a user deletes an element from the canvas or when elements are programmatically removed, indicating that the page structure has been altered. |
changed |
A general event indicating that some change has occurred within the page. It acts as a catch-all for other specific events, including modifications, insertions, deletions, or any other edits that impact the page’s current state. It’s useful for saving, versioning, or triggering custom behaviors whenever any edit is made. |
Error codes
For reference, the following error codes should be used by the server side scripting to better communicate with BuilderJS. When the server-side script returns the correct error code in the AJAX response, BuilderJS will be able to display the corresponding messages in the appropriate format.
| Error Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 400 | Bad Request -- Your request is invalid. |
| 401 | Unauthorized -- Your API key is wrong. |
| 403 | Forbidden -- The kitten requested is hidden for administrators only. |
| 404 | Not Found -- The specified kitten could not be found. |
| 405 | Method Not Allowed -- You tried to access a kitten with an invalid method. |
| 406 | Not Acceptable -- You requested a format that isn't json. |
| 410 | Gone -- The kitten requested has been removed from our servers. |
| 418 | I'm a teapot. |
| 429 | Too Many Requests -- You're requesting too many kittens! Slow down! |
| 500 | Internal Server Error -- We had a problem with our server. Try again later. |
| 503 | Service Unavailable -- We're temporarily offline for maintenance. Please try again later. |

